Here’s an opinion piece by shareholder Scott Brooksby, published in the June 10 issue of Modern Healthcare:
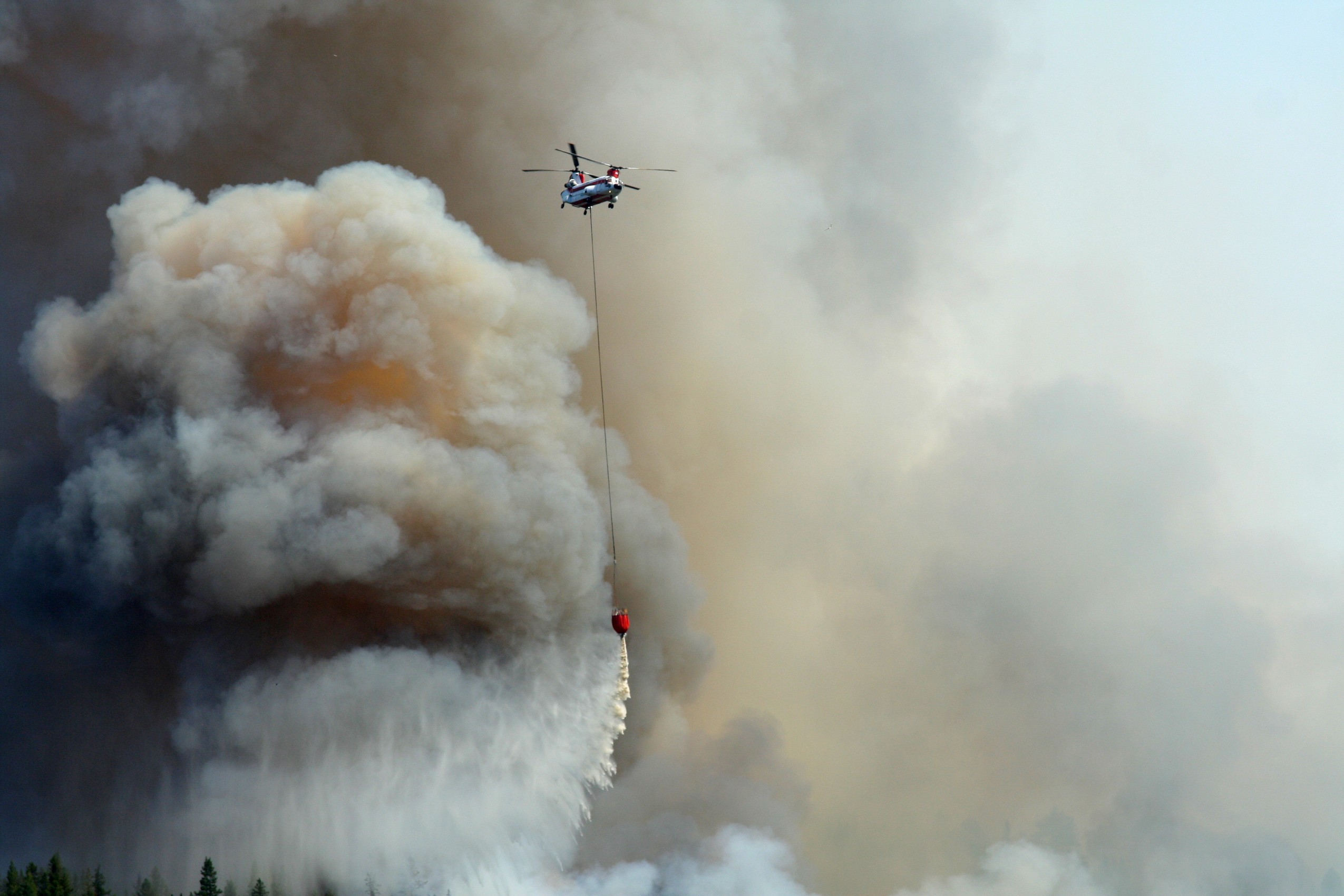
To curb medical helicopter crashes, focus on pilot haste, experience
A dramatic national conversation erupted recently following a U.S. National Transportation Safety Board finding that smart phone texting was a contributing factor in the crash of a fatal medical-helicopter flight in 2011.
The discussion has concentrated on everything from connecting the event to the dangers of texting while driving to calls for a ban on texting by pilots in air medical operations.
Absent from the discussion, however, is a larger issue that’s well recognized by helicopter industry safety organizations, and what should be of great concern for hospital administration and other organizations that contract emergency helicopter services. The issue has to do with the egregiously high incidence of fatal and critical Helicopter Emergency Medical Services (HEMS) crashes, and resulting personal injuries.
In comparison to virtually every other type of commercial aviation, there is an inordinate rate of accidents within medical helicopter aviation, with the 2010 NTSB data proof in point.
Essentially, NTSB segregates aviation operations into hundreds of categories, the largest being all U.S. major domestic air carrier flights. In 2010, NTSB reported only 14 accidents among major air carrier aviation, none of which were fatal. By contrast, in 2010 there were 13 HEMS accidents, including seven fatal crashes.
Medical helicopter pilots are heroic and driven individuals who are among the best-trained and highest-skilled pilots in the world and fly what arguably are the most dangerous missions outside of military aviation. HEMS pilots possess the grit and courage to go forth in dangerous conditions any time of night or day, in icy conditions or great heat, in storms, in densely trafficked urban controlled airspace, and remote uncontrolled airspace.
The most dangerous occupation
Operating without the benefit of formal flight plans with takeoffs and landings in uncontrolled locations ranging from roads to ball fields to the tops of buildings, the challenge is incredible. Speed is critical. But it comes with great risk. In fact, according to a University of Chicago report, crewing a medical helicopter is the most dangerous profession in America.
Clearly it takes a special individual to accept the challenge. But according to the International Helicopter Safety Team, the same attributes of risk tolerance, confidence and dogged determinism required of a HEMS pilot commonly are the very factors that, when excessive, lead to helicopter pilot error.
But what complicates the issue of haste to meet critical needs is the fact that the majority of HEMS accidents occur not when pilots are ferrying a patient to emergency treatment, but instead take place when pilots are rushing to the scene to pick up a patient, or the transportation of organs.
NTSB data shows that fully 58 percent of the 31 medical flight accidents occurring from 2007 to 2009 took place when the HEMS aircraft were en route to pick up an injured patient, or involved organ transport organs. Only 42 percent of HEMS accidents occurred with patients on board.
Haste and pilot error under harrowing conditions is exacerbated in the case of less experienced HEMS pilots. Although on the whole HEMS pilots rank among the most experienced and capable pilots in the world, NTSB records indicate that flight hours of HEMS pilots not involved in accidents have logged 19 times as much air time in a particular aircraft as those involved in accidents.
Managing contract helicopter risk
Since 2005, there has been an increasing call for greater safety requirements in HEMS aviation, focusing largely on navigation equipment and flight dispatch and monitoring systems. We expect to see continued progress in that area.
In the meantime, to reduce the incidence of HEMS crashes as well as to exercise prudent risk management, here are some steps for hospital administrators to consider:
– Review your HEMS contractor pilot training program, with a preference for programs that not only meet, but exceed, FAA compliance levels;
– Request documentation of contractor aviation risk assessment programs, and review the specific crew checklist parameters to assess risk level of each flight;
– Stipulate that pilots have a minimal level of flying hours on the specific type of aircraft to be used in life flight operations;
– Stipulate that pilots have a certain level of military flying service, or equivalent civilian training;
– Review pilot histories and encourage condition-specific training that corresponds to local conditions; and
– To limit claims against your hospital or organization, ensure that your HEMS contracts contain solid indemnity provisions.
Although the tragic human consequences of a fatal medical helicopter crash are clear, there’s less recognition of the massive risk of litigation, which while principally focused on the flight service company easily can become a deep, years-long issue for the contracting hospital organization.
HEMS operators are the first line of defense in one of the greatest challenges of emergency care, operating under diligent training execution and best principles of safe flight as established by the FAA and contractor safety policies. However, perfection is an aspiration, and recognizing the record of accidents, hospital organizations should look beyond smart phone bans to limit the occurrence and risk of medical helicopter accidents.


